Introduction
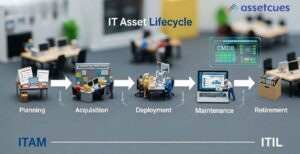
The IT asset management lifecycle tracks and optimizes assets from purchase to disposal. It spans planning, acquisition, deployment, maintenance, and eventual retirement or disposal. Moreover, following best practices at each stage maximizes value and ensures compliance. In ITIL, lifecycle management aligns ITAM with ITSM using a centralized CMDB.
Explore how managing assets across their full lifecycle—from purchase to disposal—improves ROI, compliance, and operational efficiency.
Why does this matter? Global IT spending keeps rising (projected around $5 trillion in 2024), making cost optimization more critical than ever. Strategic ITAM can help rein in expenses – effective IT asset management practices can cut overall IT spending by an estimated 15–20% through lifecycle optimization. A well-managed IT asset lifecycle gives organizations tighter control over assets, leading to less waste and more value from IT investments.
Understanding the IT Asset Management Lifecycle (ITAM & ITIL Basics)
The IT asset management lifecycle spans from initial planning to final disposal of an asset. Both ITAM best practices and the ITIL framework stress managing assets through each stage to maximize efficiency and value. Whether we call it the IT asset lifecycle or IT asset life cycle, the idea is proactive management from cradle to grave.
-
Key Stages of the IT Asset Lifecycle:
There are five main stages in an IT asset’s life: Planning & Inventory, Procurement (Acquisition), Deployment (Installation), Maintenance (Operation), and Retirement (Disposal). Each stage must be handled carefully to optimize asset value and avoid surprises.
Explore the key stages of the asset lifecycle>>
How to Track IT Assets from Purchase to Disposal
To prevent assets from slipping through gaps, implement a structured lifecycle process. Plan in advance by recording assets before purchase and updating details immediately. Moreover, update the CMDB during deployment, then monitor and maintain assets continuously. Finally, retire assets properly by wiping data, removing from service, and updating records.
Best Practices for Effective IT Asset Lifecycle Management
Applying best practices at each stage of the lifecycle makes IT asset management more efficient and strategic. Here are some key practices aligned with ITAM principles and ITIL guidelines:
-
Establish a Clear ITAM Policy & Governance:
Set formal policies for how assets are requested, approved, used, and retired. Define who is responsible for each stage of the lifecycle, and align these rules with frameworks like ITIL for consistency. Strong governance brings consistency and prevents ad-hoc handling of assets.
-
Maintain a Centralized Asset Repository (Integrate a CMDB):
Use one system of record – ideally a CMDB – to track all assets and their details. Update it in real time as assets move through stages so that each asset’s full history is recorded (sometimes called the “CMDB lifecycle” of an asset). A single central repository ensures IT, finance, security, and other stakeholders are all referencing the same up-to-date data.
-
Perform Regular Audits and Compliance Checks:
Schedule periodic audits of your hardware and software inventory. Physically verify that listed devices exist and are in the right location, and ensure software usage matches your license entitlements. Regular audits catch discrepancies – for example, “ghost assets” that were disposed of but never recorded – before they cause problems. This practice also prepares you for external vendor audits and avoids surprise compliance penalties.
-
Optimize Asset Utilization & Lifespan:
Continuously monitor asset usage to identify underutilized or obsolete resources quickly. If hardware sits idle or licenses go unused, reallocate or consolidate effectively. Additionally, extend asset life through updates, patching, cleaning, and component upgrades. Finally, track utilization and ROI to decide when retirement or replacement is necessary.
-
Foster Cross-Team Collaboration & Training:
Involve all stakeholders like IT, procurement, finance, and security in asset management. Regular communication ensures awareness of server replacements or software renewals, avoiding surprises. Additionally, train employees on requesting, maintaining, and returning assets responsibly. When everyone follows procedures, the risk of lost or misused assets decreases.
Implementing these best practices transforms asset management from a reactive task into a proactive strategy. As a result, organizations cut costs by removing redundant assets and avoiding wasteful purchases. Moreover, compliance improves, risks decrease, and operations run more efficiently overall. Ultimately, optimizing the asset lifecycle drives savings and strengthens business performance significantly.
How Automation and Tools Streamline the IT Asset Lifecycle
Modern ITAM and ITSM tools automate lifecycle tasks, saving time and reducing errors. For instance, discovery tools detect new devices, creating asset records automatically. Integrated systems populate purchase details and assignments instantly, eliminating manual data entry. Furthermore, automation pushes configurations, monitors health, tracks warranties, and triggers retirement workflows.
By integrating these automated actions, you maintain accurate, up-to-date asset information across your organization. Everyone – from the service desk to finance – works from the same source of truth, and fewer assets slip through the cracks. In short, leveraging the right tools makes managing the IT asset lifecycle more efficient and reliable.
Aligning the IT Asset Lifecycle with ITIL Practices and CMDB
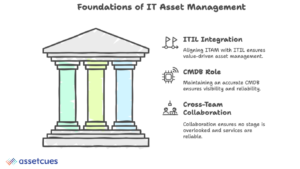
A successful IT asset management program works hand-in-hand with ITIL best practices and a well-maintained CMDB. Aligning the asset lifecycle with ITIL processes (and keeping the CMDB updated) ensures that asset data supports your IT services and encourages cross-team collaboration.
-
ITAM and ITIL Integration:
ITIL asset lifecycle management follows the same multi-stage approach as general ITAM, ensuring assets are planned, used, and retired in a controlled, value-driven way that supports the business.
-
The Role of the CMDB:
In ITIL, the CMDB tracks configuration items and their relationships throughout lifecycles. Maintaining accuracy ensures visibility into asset location, configuration, and dependencies. For example, before retiring a server, the CMDB highlights linked applications to prevent outages. Therefore, updating it at each stage—ideally through automation—supports reliable incident and change management.
-
Cross-Team Collaboration (ITAM + ITSM):
Aligning IT asset management with ITIL naturally involves multiple teams working together. Breaking down silos between asset managers, the service desk, security, finance, and other groups ensures no stage is overlooked and everyone is aware of upcoming asset changes. This collaboration leads to more reliable services, smoother workflows, and fewer last-minute crises.
Also learn how to manage the fixed asset lifecycle for audit accuracy>>
FAQ’s
Q: What is the difference between IT asset management and a CMDB?
A: IT Asset Management (ITAM) is the practice of tracking and optimizing IT assets throughout their lifecycle. A CMDB is a database storing asset details and their relationships. Simply put, ITAM is the process, while the CMDB is the supporting system. The CMDB centralizes inventory, but ITAM also includes policies, procedures, and people.
Q: Why is IT asset lifecycle management important in ITIL?
A: In ITIL, effective asset lifecycle management ensures hardware and software remain reliable and valuable. It aligns assets with service delivery, reducing disruptions and avoiding costly issues. Moreover, timely retirement prevents risks related to security, compliance, or unnecessary expenses. Ultimately, lifecycle management maximizes value and minimizes failures or compliance surprises.
Q: How often should we audit our IT asset inventory?
A: Audit your IT asset inventory at least annually, or more often for critical assets. Many organizations perform quarterly or continuous checks using discovery tools. Regular audits keep CMDB or ITAM records accurate and eliminate ghost assets. Therefore, establish a consistent schedule, combining software true-ups and hardware audits.
Q: What are some tools for IT asset lifecycle management?
A: Common tools include IT Asset Management software and ITSM platforms with asset modules. For example, ServiceNow ITAM, Jira Service Management, Microsoft Endpoint Manager, Flexera, and Device42. These tools automate inventory updates, track assets across stages, and integrate with the CMDB. Therefore, prioritize features like auto-discovery, license management, workflow automation, and ITIL process integration.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Diligently managing assets through their lifecycle – with clear processes, the right tools, and ITIL alignment – turns IT asset management into a strategic advantage.
The payoff is clear: lower costs by cutting waste and avoiding unnecessary purchases. Service reliability improves by repairing or replacing equipment before unexpected failures occur. Moreover, stronger security and compliance come from proper asset tracking and end-of-life handling. Ultimately, excelling at IT asset lifecycle management saves money and ensures consistent technology support.
Now is the time to elevate your IT asset management approach. By putting these lifecycle strategies into action – and leveraging automation and modern tools where appropriate – you can optimize your IT asset investments while reducing hassle and risk.









