Asset movement refers to the tracking of any item, like equipment or inventory, as it changes location or possession within a company. This can involve several scenarios: transferring an asset between different offices, assigning an asset from storage to a specific employee, handing over equipment between employees for a project, and finally, returning a company asset from an employee back to its designated storage location.
By effectively tracking these movements, organizations can maintain control of their assets, improve utilization, and minimize loss or theft. For a deeper understanding of how tracking plays a critical role in managing assets across their lifecycle, check out our detailed blog on “Asset Tracking: The Ultimate Guide for Finance, IT, and Operations”.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore the significance of asset movement control. Additionally, we provide practical insights on efficiently tracking and managing your assets. We will also examine how RFID, GPS, IoT, and BLE enhance asset verification and control.
Keeping Tabs on Your Assets: Why Movement Control is Key.
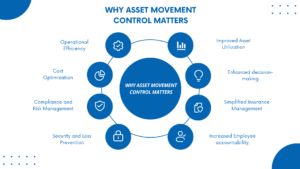
Here are some key reasons why asset movement control matters:
- Operational Efficiency: Effective asset movement control ensures assets are available when needed. As a result, it minimizes operational disruptions and delays.
- Cost Optimization: By closely monitoring asset movements and maintenance schedules helps reduce operating costs. This leads to more efficient asset management.
- Compliance and Risk Management: Controlling asset movement ensures compliance with regulatory requirements. Thus, it reduces the risk of legal and financial issues.
- Security and Loss Prevention: Asset movement control systems detect unauthorized movements. Consequently, they reduce the risk of theft and asset loss.
- Improved Asset Utilization: Knowing where assets are located and who is using them allows for better planning and resource allocation. This prevents underutilized assets sitting idle and ensures critical equipment is readily available.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Data gathered through asset movement tracking provides valuable insights into asset usage patterns. This information can be used to make informed decisions about asset purchases, maintenance schedules, and potential upgrades.
- Simplified Insurance Management: Proper asset tracking streamlines insurance claims by providing accurate documentation of asset ownership, location, and condition. This can lead to faster claim processing and potentially lower insurance premiums.
- Increased Employee Accountability: Knowing their movements are tracked can encourage employees to handle assets with greater care and responsibility. This can lead to fewer accidental damages and a longer lifespan for valuable equipment.
Since we’ve established the value of controlling asset movement, let’s delve into the essential features.
Must-Have Features for Tracking Your Assets:
1. Real-Time Tracking
A robust asset movement control system should provide real-time tracking capabilities. It should allow you to monitor the current location and status of assets as they move within your organization.
2. Geofencing
Geofencing is crucial for controlling asset movement within defined boundaries or zones. The system allows you to set virtual geographic boundaries, triggering alerts when assets cross them.
3. Alerts and Notifications
Proactive alerts and notifications are essential for asset movement control. The system should notify you immediately when unauthorized movements are detected, allowing for swift action to prevent potential issues.
4. User Authorization
User authorization features ensure that only authorized personnel can move assets. The system should allow you to set permissions and restrictions on who can move specific assets and under what conditions.
5. Reporting and Analytics
Comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities are critical for gaining insights into asset movements. The system should generate detailed reports on asset locations, movements, and usage patterns, enabling data-driven decision-making.
6. Integration
Seamless integration with other systems and software within your organization is vital. It should allow for easy data sharing and coordination with other business processes.
Now that we’ve explored the essential features of an asset movement control system, let’s check some of the technologies that can enhance asset verification and control.
Unlock Greater Control
Over Your Asset Lifecycle
From acquisition to disposal, ensure your assets are exactly where they’re supposed to be.
Unlock Greater Control
Over Your Asset Lifecycle
From acquisition to disposal, ensure your assets are exactly where they’re supposed to be.
Leveraging Technology for Asset Movement Control
The advancements in technology have introduced innovative ways to enhance asset movement control. Businesses can leverage various technologies to streamline asset verification and control processes.
Let’s explore some of these cutting-edge technologies and their applications in asset movement control:
1. Barcode
Barcode technology is a system for representing information in a visual, machine-readable format. It uses bars and spaces of varying widths to encode information visually. A barcode reader then scans and translates this pattern into usable data.
Here’s a closer look at how barcode technology works:
- Scanning: Barcode scanners use a light source, typically a laser, to illuminate the barcode. The reflected light is then captured by a light sensor in the scanner.
- Decoding: The scanner transmits decoded data to a computer system for further processing. Then, the system uses this data to track inventory, manage assets, or handle transactions.
Barcode technology is a mature and reliable solution for a wide range of asset tracking and data collection applications.
2. RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification)
RFID technology is a game-changer in asset movement control. It operates by using radio-frequency signals to track and identify assets. Here’s how RFID technology can be applied:
- Tagging: Assets are tagged with RFID tags or labels, each containing a unique identification code.
- RFID Readers: RFID readers are strategically placed at checkpoints or exit points. They communicate with RFID tags and capture data about asset movements.
- Automated Tracking: As assets enter or exit RFID-enabled areas, RFID readers automatically record their movements in real time.
- Unauthorized Movement Detection: RFID systems can trigger alerts or notifications when unauthorized asset movements occur.
RFID technology enables precise and efficient asset tracking across various industries. Therefore, it is ideal for sectors requiring accurate control, like healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing. Learn more about RFID-based asset movement tracking in our detailed blog on “RFID Asset Tracking – Transforming Asset Management”.
3. GPS (Global Positioning System) and IoT (Internet of Things)
GPS and IoT technologies provide powerful tools for tracking mobile assets and controlling their movements. Here’s how they enhance asset movement control:
- Geofencing Through GPS: Organizations can implement geofencing using GPS technology. Virtual geographic boundaries are defined, and when assets equipped with GPS technology cross these boundaries, immediate alerts are generated.
- IoT Sensors: IoT sensors can be embedded in assets to monitor their condition and location in real-time. These sensors collect data on factors like temperature, humidity, and motion. If predefined thresholds are exceeded, alerts can be triggered, allowing for proactive maintenance.
GPS and IoT technologies are valuable for businesses with mobile assets like fleets and equipment. As a result, organizations maintain control and efficiently optimize asset utilization.
4. BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) Beacons
Organizations increasingly use BLE beacons for indoor asset tracking and movement control. These beacons actively emit low-energy Bluetooth signals, which nearby devices—like smartphones or receivers—detect and process. Here’s how BLE technology supports accurate asset movement control:
- Indoor Navigation: BLE beacons create indoor navigation systems in large facilities or warehouses with weak GPS signals. Employees or visitors can then use their smartphones to navigate and locate specific assets.
- Security and Zone Control: In highly sensitive environments, BLE beacons can be attached to assets containing hazardous substances. Zones are designated within the facility, and BLE readers are installed at entry points. If unauthorized assets come too close to restricted zones, BLE readers trigger alarms and alerts.
5. RTLS (Real-Time Locating System)
RTLS provides real-time location data for objects and people in indoor environments. In contrast, GPS relies on satellites and works best in outdoor settings. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
- Tiny Tags, Big Impact: Small tags are attached to the items or worn by personnel you want to track. These tags transmit signals using technologies like radio waves (RFID), ultrasound, or even light.
- A Network of Listeners: Strategically placed readers or sensors throughout the area pick up the signals from the tags.
- Putting the Pieces Together: A central system receives data from readers and interprets signals using RTLS technology. Then, it pinpoints the exact location of the tagged item or person in real time.
- Real-Time Visibility: The software displays location data in real-time, giving you a clear view of each asset’s exact position.
RTLS can be a valuable tool for optimizing operations, improving efficiency, and gaining valuable insights within your indoor environment.
Conclusion
Asset movement control is essential for organizations to maintain visibility, reduce losses, and improve asset utilization. Therefore, implementing a reliable system with real-time tracking, geofencing, and user authorization becomes vital. Moreover, integrating technologies like RFID, GPS, and BLE beacons significantly enhances tracking accuracy and responsiveness.
As a result, businesses can streamline workflows, avoid asset misplacement, and reduce theft. In conclusion, effective asset movement control enables smarter decision-making, boosts operational efficiency, and ensures long-term asset protection..
Take Control of Your Asset
Movements Today
Implementing effective asset movement control strategies can significantly
enhance your organization’s efficiency and security.
Take Control of Your Asset
Movements Today
Implementing effective asset movement control strategies can significantly
enhance your organization’s efficiency and security.
FAQs
Q. What is asset movement?
A. Organizations track assets as they move between locations, departments, or employees. As a result, they maintain accurate records and improve accountability.
Q. How do you track asset movement?
A. AssetCues uses RFID, GPS, BLE, an RTLS to monitor asset movement in real time. Moreover, the system sends alerts, applies geofencing, and logs every asset transfer automatically.
Q. Why is asset movement control important?
A. Asset movement control isn’t just about security, it’s about efficiency too. By tracking your assets, you ensure they’re readily available, minimizing downtime. This also helps optimize usage and maintenance schedules, saving money. Plus, it keeps you compliant with regulations and helps prevent theft or loss of your valuable equipment and inventory.
Q. How can I get started with asset movement control?
A.
- Identify your needs: What assets do you need to track? What features are most important?
- Research different systems: Consider features, budget, and ease of use.
- Implement a pilot program: Test a system with a small group of assets before full deployment.
- Train your employees: Ensure everyone understands the system and procedures.
By implementing effective asset movement control, organizations can gain better control of their assets, optimize operations, and make data-driven decisions.
Q. How can technology improve asset movement control?
A. Technologies like RFID use radio waves for automated tracking via tags and strategically placed readers. Additionally, GPS and IoT offer real-time location data and condition monitoring for mobile assets through satellite and sensor integration. Moreover, BLE beacons emit low-energy Bluetooth signals for indoor navigation and zone control, enhancing asset visibility within facilities. As a result, these advancements work together to create a comprehensive asset movement control ecosystem.




