Accuracy, availability, and traceability of company assets is important for operational efficiency and financial integrity. The ability to quickly locate and verify each asset is essential for better management of physical assets. That’s where asset tagging and management become critical for businesses.
Implementing asset tagging solutions, from asset barcodes to advanced RFID systems, enhances asset visibility. It reduces human error and ensures compliance with auditing and regulatory standards. Asset tagging streamlines identification and tracking, minimizing manual record-keeping.
Asset tagging plays a pivotal role in asset management by streamlining how assets are identified and monitored. It greatly reduces the need for tedious manual record-keeping. Companies that adopt asset tagging often experience faster audits and fewer instances of lost equipment. It also leads to improved data quality, supporting better decision-making across asset management processes.
This guide covers best practices for asset tagging and compares methods like barcodes versus RFID. It outlines implementation steps, key considerations, and the benefits of a strong tagging strategy. Effective deployment enhances asset lifecycle management, boosts productivity, and reduces risks of lost or stolen assets. Let’s dive in!
What is Asset Tagging?
Asset tagging is the practice of assigning a unique identifier to physical assets. Labels such as asset barcodes, QR codes, or RFID tags are affixed for tracking. These identifiers link assets directly to corresponding entries in the asset register.
An asset tag can be easily scanned using an asset tagging solution or system. This enables quick identification and lifecycle management, preventing loss or theft. For instance, barcode tags or RFID tags on laptops, vehicles, and machinery streamline asset management.
Scanning an asset tag instantly provides details like ownership, location, and maintenance history. Asset tags vary from simple barcode stickers to durable metal fixed asset tags. Automated fixed asset tagging eliminates reliance on memory or manual logs.
Employees can effortlessly retrieve or update asset data by scanning tags. This greatly enhances accuracy and efficiency during audits and asset transfers.
Why is Asset Tagging Important?
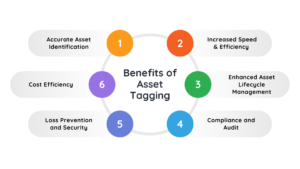
Asset tagging is crucial for efficient asset management and improved operational control. It reduces errors, saves time, and lowers costs significantly. Here are key benefits of asset tagging:
- Accurate Asset Identification: Each asset receives a unique identifier for precise tracking. This eliminates manual record-keeping errors and ensures accurate asset records.
- Increased Speed & Efficiency: Manual asset audits can take considerable time, depending on asset count. Automated asset tagging reduces this duration dramatically. With scanners and software, asset verification occurs rapidly and efficiently.
- Enhanced Asset Lifecycle Management: Asset tags connect assets to their digital profiles, including maintenance schedules. This supports comprehensive management from procurement to disposal.
- Compliance and Audits: Accurate asset records are crucial for regulatory compliance and financial reporting. Asset tagging ensures updated records, simplifying compliance audits and reducing errors.
- Loss Prevention and Security: Real-time tracking and quick identification provided by asset tagging deter theft. Knowing each asset is tagged and traceable reduces unauthorized removals.
- Cost Efficiency: Asset tagging optimizes resource utilization and minimizes errors. Quick scans reduce manual efforts, prevent mistakes, and save labor costs.
These benefits lead to enhanced accountability and greater operational efficiency. Employees spend less time managing asset records and more time on productive tasks. Reliable asset data builds management confidence, making asset tagging essential for businesses.
Asset Tagging vs. Asset Marking: What’s the Difference?
Asset tagging is a specific type of asset marking, but these terms differ slightly. Asset marking broadly refers to assigning identifiers to assets, either directly or via tags. Direct marking methods include engraving or stamping IDs onto equipment.
- Direct asset marking provides permanent, tamper-resistant identification directly on items. It is ideal for assets subject to harsh conditions, like heavy machinery or tools. These permanently engraved or stamped identifiers withstand wear and last long.
- Asset tagging uses external identifiers such as barcode labels, RFID, BLE, or GPS tags. These tags enhance tracking efficiency, enabling automated scanning and real-time updates. Tags facilitate quick physical audits and easy asset location tracking.
Real-Time Asset Movement Tracking with Asset Tagging
Asset tagging enhances real-time tracking of asset movements, going beyond simple verification. By combining tags with RFID, GPS, or IoT sensors, companies significantly increase visibility. They track asset locations, detect unauthorized movements, and improve overall security. Mobile equipment like IT devices, vehicles, and hospital tools especially benefit from this approach.
Geofencing with RFID and GPS
Asset tags integrated with geofencing create virtual boundaries around defined areas. For instance, equipment assigned to a specific building triggers alerts if moved. GPS asset tags are ideal outdoors, instantly notifying deviations from designated routes.
RFID Zone Monitoring
RFID readers at entry or exit points automate asset movement logging. Fixed gateways record asset check-ins and check-outs without manual intervention. This approach significantly reduces tracking efforts and enhances security against unauthorized movements. RFID monitoring also helps identify after-hours asset transfers or suspicious activities quickly.

White Paper
Automate recording of Asset check-in and checkout using RFID Technology. Download our latest white paper to learn how to implement and benefit from automation
White Paper
Discover how AssetCues automates asset verification and management in SAP, enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and compliance. Learn more about our SAP Certified Solution!

Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS)
Real-Time Location Systems provide continuous location updates for indoor tagged assets. These systems combine RFID, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi sensors to precisely track assets. For example, hospitals use RTLS to quickly locate medical equipment in real-time.
Asset Utilization Insights
Tracking movements over time generates valuable asset utilization reports. Asset tagging solutions analyze usage patterns effectively, highlighting frequently or rarely used items. These insights help optimize asset allocation, maintenance scheduling, and future investment decisions.
Security and Loss Prevention
Real-time tracking significantly improves asset security and prevents losses. Immediate alerts on unauthorized movements enable swift investigation and response. Visible tagging systems also deter internal theft and greatly aid asset recovery efforts.
Challenges and Considerations in Asset Tagging Implementation
Implementing asset tagging brings major benefits but requires careful planning. Addressing key challenges proactively ensures a smooth and successful rollout. Below are essential considerations for effective asset tagging and management:
Availability of Accurate Asset Data
An accurate asset register is essential before starting asset tagging. Incomplete or inaccurate records initially cause confusion and errors during implementation. Issues like duplicate entries or unlisted assets complicate the tagging process. Clean and verify your asset data first to ensure successful implementation.
Choosing the Right Tagging Technology (Barcode vs. RFID)
Selecting the best tagging technology depends on your needs and budget. Barcode tags or asset barcodes are cost-effective and easy to generate. However, they require direct line-of-sight scanning for identification. RFID tags are more advanced, allowing scanning without direct visibility of assets.
Choosing Durable Asset Tags
Selecting durable tags suited to your assets’ environments is crucial. Consider tag materials based on exposure to heat, chemicals, abrasion, or outdoor conditions. Durable equipment asset tags or fixed asset tags maintain readability over time. As a result, quality tags ensure your asset tagging solution remains effective long-term.
Selecting the Right Asset Tagging Services Provider
To begin with, evaluate asset tagging services based on geographic coverage and industry expertise. Additionally, assess their capability in asset baseline creation and asset reconciliation processes. Next, review their available asset tags and experience serving companies similar to yours. Ultimately, a proven provider ensures smooth implementation and ongoing support.
Choosing the Best Asset Tagging Software
Choosing the right asset tagging software means matching features to your specific requirements. To begin with, look for mobile applications, automation, reporting analytics, user-friendly interfaces, and integration compatibility. In turn, effective asset tagging software simplifies asset management, reduces errors, and boosts efficiency.
Maintenance of Tags and Data
Regular maintenance of asset tags and data ensures continued effectiveness. Tags can deteriorate over time, becoming damaged or unreadable. Therefore, establish routine inspections during regular audits. Replace worn or missing tags promptly to avoid data gaps. Consistent maintenance protects the accuracy and reliability of your asset data.
By addressing these key considerations upfront—accurate data, suitable technologies, durable tags, quality service providers, effective software, and regular maintenance—your asset tagging implementation will be effective and sustainable.
Also read our comprehensive guide on Implementing Asset Tagging System>>
Asset Tag Number: Use Asset ID or a Separate Tag Number?
When designing asset tags, a common question arises regarding tag numbering. Should you print existing asset IDs or create separate, new tag numbers? The best practice is to assign separate tag numbers linked to your database.
Here are several advantages of using separate tag numbers:
Logistical Efficiency
- Generic, pre-numbered tags can be applied easily to any asset.
- No need to match specific asset IDs to tags during deployment.
- This simplifies the tagging process, saving considerable time and effort.
Minimizing Tag Wastage
- Printing tags with specific asset IDs often results in unused or wasted tags.
- Unexpected scenarios like disposed assets can cause gaps in tag sequences.
- Generic numbering prevents wastage, improving overall resource utilization.
Reduced Identification Errors
- Printing specific asset IDs risks incorrect tag placements during tagging.
- Mistakes like placing asset #105’s tag on asset #501 are difficult to detect.
- Separate numbering reduces errors and maintains accurate asset tagging records.
Flexibility with Asset Changes
- Assets may be renumbered or reclassified during reorganizations or database merges.
- Tags with internal IDs require replacement, creating additional labor and costs.
- Using separate tag numbers allows flexibility without frequent tag replacements.
Adopting separate tag numbers supports efficient, accurate, and flexible asset tagging practices.
Cost vs. ROI of Asset Tagging
Businesses weighing asset tagging implementation typically evaluate upfront costs against ROI. Though initial expenses are involved, asset tagging consistently provides significant long-term returns. Here’s a breakdown of costs and offsetting benefits:
Upfront Costs
Initial expenses include asset tags, ranging from inexpensive barcode labels to RFID tags. In addition, additional hardware purchases may include barcode scanners, RFID readers, antennas, or mobile scanning devices. Furthermore, software costs include licenses for the best asset tagging software or integrations with existing systems. Lastly, companies may also incur short-term expenses by hiring external asset tagging service providers.
Operational Savings
Asset tagging immediately improves operational efficiency by reducing manual labor significantly. Moreover, automated tracking saves considerable time that was previously spent on asset inventory and equipment locating. As a result, employees freed from manual tracking tasks can focus on more valuable and productive activities. Ultimately, these efficiency improvements effectively increase productivity without additional staffing costs.
Loss Prevention and Asset Utilization
Reducing asset loss, theft, and misplacement significantly boosts asset tagging ROI. As a result, companies often avoid unnecessary equipment or spare asset purchases. Indeed, many companies over-purchase due to uncertainty about current inventory levels. Therefore, asset tagging solutions offer clear visibility into all available assets. Consequently, they help prevent unnecessary duplicate purchases and reduce excess inventory. Moreover, clear inventory data enables optimized asset utilization across departments. In turn, optimized utilization helps reduce overall spending and minimize waste.
Long-Term ROI
The value of asset tagging grows substantially with scale and asset volume. As a result, manual asset tracking becomes increasingly costly and inefficient as organizations expand. Consequently, many companies find that asset tagging solutions pay for themselves within one to two years. In the long run, ROI is realized through labor cost savings, reduced asset losses, and enhanced decision-making capabilities.
Asset tagging proves to be a wise long-term investment, combining cost-efficiency, accuracy, and improved operational control.
Curious How Asset
Tagging Works ?
From Tag Placement - Tag Scanning - Real-Time Reporting
Curious How Asset
Tagging Works ?
From Tag Placement – Tag Scanning – Real-Time Reporting
Conclusion
Asset tagging is essential for streamlined asset tagging and management. By attaching unique identifiers and integrating them with asset management software, organizations can significantly enhance tracking reliability. Furthermore, selecting appropriate tagging technology and durable materials ensures effective and long-lasting asset tags.
Though initial implementation involves upfront costs, asset tagging quickly delivers valuable ROI. Key benefits include faster audits, reduced errors, improved data accuracy, and minimized asset losses. Ultimately, investing in asset tagging solutions significantly boosts organizational efficiency and financial integrity.
FAQs
Q. Which assets should be tagged in a company?
A. Organizations should tag all physical assets listed on their balance sheets. Specifically, these assets typically include fixed assets and IT equipment, such as computers, servers, machinery, vehicles, and furniture.
Q. Which is better for asset tagging: barcodes or RFID?
A. Both barcode tags and RFID tags have distinct advantages. For instance, asset barcode labels are inexpensive, simple to implement, and easy to scan. On the other hand, RFID tags use wireless scanning without a direct line-of-sight. Therefore, enable bulk scanning, which is ideal for larger inventories.
Q. Is asset tagging worth the cost for my business?
A. Asset tagging typically offers a strong ROI; therefore, it is well worth the upfront costs. In fact, the initial expenses for tags, scanners, software, and labor are quickly recovered through efficiency gains. Moreover, asset tagging drastically reduces audit durations, minimizes asset loss, and significantly improves operational control.
Q. What are asset tagging services, and should we use them?
A. Asset tagging services are professional providers that specialize in tagging and tracking company assets. These services supply customized asset tags and physically tag each asset. They also establish and configure your complete asset database. As a result, companies with large or dispersed asset bases benefit significantly from using asset tagging services.
Q. What is the best asset tagging software?
A. Ultimately, the best asset tagging software depends on your organization’s unique requirements. Ideal asset tagging software features include user-friendly data entry, barcode or RFID integration, and detailed asset categorization. In addition, they should offer real-time tracking and robust reporting for efficient asset management.




