Asset tagging has become a critical component for organizations seeking to enhance asset visibility, streamline physical verification, and ultimately improve operational efficiency. This guide provides a step-by-step approach for implementing an asset tagging system that complements our previous blog on “Asset Tagging and Management – Best Practices & Implementation Guide”, It is designed for fixed asset managers, finance managers, IT managers, facilities managers, and business leaders looking to deploy a robust asset tagging solution. By following a structured process, organizations can reduce asset loss, enhance compliance, and improve overall ROI.
What Is an Asset Tagging System?
An asset tagging system automates asset tracking and management by assigning each asset a unique identifier. It simplifies the process of physical verification, reduces manual errors, and integrates with digital asset registers to provide real-time data on asset location, condition, and lifecycle status.
Overview of Asset Tracking Technologies
Barcode/QR Code Tagging
- Barcodes encode basic data and are scanned using a handheld device, making them ideal for static assets.
- QR Codes store more information and can link to digital records, enhancing traceability and integration with other systems.
RFID Asset Tagging
- Uses radio waves to read tags without direct line of sight.
- Passive RFID tags are cost-effective and activated by a reader, while active RFID tags include a battery for longer range and automated, rapid data capture.
GPS Tracking
- Provides real-time location data via satellite signals, making it perfect for monitoring mobile or outdoor assets like vehicles.
- Typically more expensive and power-intensive.
BLE Tracking
- Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) offers a low-power, short-range solution suitable for indoor or localized tracking.
- Cost-effective and easily integrated with smartphones, though with less range and precision compared to RFID or GPS.
Features of a Good Asset Tagging System
A robust asset tagging system not only captures asset data accurately but also integrates seamlessly with existing business operations. Here are the critical features that distinguish a superior asset tagging system:
Mobile Application Capability
- A leading system includes a dedicated mobile app that enables on-the-go tagging, scanning, and data capture. This app should support high-resolution image capture, geolocation, and immediate data synchronization, ensuring that field personnel can tag assets quickly and accurately.
Asset Componenting & Grouping
- The system should allow for granular tagging by supporting the tagging of individual components as well as grouping related, non-taggable items under a parent asset. This flexibility helps create a detailed asset hierarchy, facilitating better management and tracking of complex asset assemblies.
Prebuilt ERP Connectors
- Integration is key. A good asset tagging solution offers out-of-the-box connectors to popular ERP systems (like SAP, Oracle, or Microsoft Dynamics), ensuring that asset data flows seamlessly between the tagging system and your enterprise software, reducing manual entry errors and speeding up decision-making.
Configurable Review Workflows
- To maintain data integrity, the system should include a configurable workflow that allows asset managers to review, verify, and approve tagged asset data. This built-in quality control helps catch inconsistencies early and ensures that the asset register remains accurate.
Offline Functionality
- For environments with unreliable connectivity—such as remote locations or large industrial facilities—the ability to tag assets offline is crucial. The system should cache data locally and sync automatically once connectivity is restored, ensuring continuous operations.
Scheduled Audits & Maintenance
- A comprehensive asset tagging system supports periodic physical audits. It should enable scheduling of audits, prompt reminders for inspections, and allow for the updating or replacement of tags. This ensures that asset data remains current and accurate over time.
Analytics & Reporting
- Insightful analytics are essential for proactive asset management. The system should offer customizable dashboards and reporting features that highlight key metrics like asset aging, missing or at-risk assets, and audit performance. These analytics empower managers to make data-driven decisions and optimize asset utilization.
Broad Technology Integration
- The ideal system integrates seamlessly with various tracking technologies (barcodes, QR codes, RFID, GPS, BLE) and supports a wide range of hardware vendors. This versatility allows organizations to tailor the asset tagging solution to different asset types and operational environments, ensuring that the system grows with your business.
Learn more about the 6 Reasons Why Tagging of Assets is Important>>
Transform your asset management with precise tagging and automated verification with AssetCues
Transform your asset management with precise tagging and automated verification with AssetCues
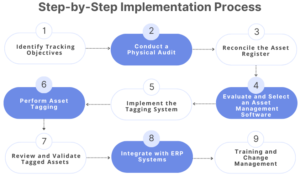
Step-by-Step Implementation Process
Implementing an asset tagging system requires careful planning and execution. Below is a detailed, research-backed guide to ensure a smooth deployment:
Identify Tracking Objectives
- Define specific goals such as automating physical verification, tracking asset movement, or meeting regulatory compliance.
- Determine which assets require tagging and decide whether a single technology or a hybrid approach is needed based on asset type and operational environment.
Conduct a Thorough Physical Audit
- Perform a complete physical inventory of assets to validate your current baseline.
- Classify assets by value, location, usage, and environmental conditions. This step helps in selecting the appropriate tag type (e.g., durable metal tags for heavy equipment, non-metal asset tag for laptops).
Reconcile the Baseline with the Asset Register
- Compare your physical audit results with the existing asset register.
- Update the register to reflect any discrepancies and establish a clean baseline for the tagging process.
Evaluate and Select an Asset Management Software
- Research multiple asset management products and ensure that at least a few options meet your criteria.
- Evaluate key features, integration capabilities, and scalability. Consider solutions that offer comprehensive tagging features—AssetCues is one such leader with compelling capabilities.
Implement the Tagging System
- System Setup: Install the chosen software and configure it to align with your asset management processes.
- Integration: Connect the system with your ERP or asset register to ensure seamless data flow.
- Tag Production: Determine the material, printing, and affixing technology that matches the asset’s lifecycle. This decision affects durability and readability.
Perform Asset Tagging
- Deploy tags using best practices: affix tags in optimal, visible locations using secure fixing methods.
- Utilize the mobile application to capture asset photos, record geolocation data, and enter additional physical information during the tagging process.
Review and Validate Tagged Assets
- Conduct a rigorous review to verify that each tag is accurately recorded in the asset register.
- Resolve any discrepancies immediately to prevent long-term data inaccuracies.
Integrate with ERP Systems
- Finalize the process by integrating asset tag numbers into your ERP.
- Ensure that the asset management system updates in real time with any changes made during tagging or audits.
White Paper
Discover how AssetCues automates asset verification and management in SAP, enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and compliance. Learn more about our SAP Certified Solution!

White Paper
Discover how AssetCues automates asset verification and management in SAP, enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and compliance. Learn more about our SAP Certified Solution!

Training and Change Management
- Provide comprehensive training to all users—ensuring that they are proficient with the new system, especially the mobile app and review workflows.
- Communicate changes across departments to secure adoption and mitigate resistance.
Post-Implementation Strategies
Ongoing Asset Tagging & Periodic Audits
Regular Audits:
- Schedule periodic reviews to ensure asset data remains accurate and current.
Tag Maintenance:
- Establish protocols for inspecting and replacing damaged or worn tags.
Performance Metrics
Monitor KPIs:
- Track key indicators such as reduced audit time, decreased asset loss incidents, and improved data accuracy.
Automated Reporting:
- Use reports to identify performance gaps and areas for further optimization.
Feedback & Continuous Improvement
User Feedback:
- Encourage staff to provide feedback on system usability and identify any challenges.
System Upgrades:
- Regularly update the asset tagging system based on technological advancements and user suggestions.
Future Trends in Asset Tagging Systems
IoT and Smart Tagging
Real-Time Analytics:
- Integration with IoT devices allows continuous monitoring and immediate decision-making.
Enhanced Data Capture:
- Smart tags can record environmental data, aiding in predictive maintenance.
AI and Predictive Analytics
Proactive Maintenance:
- AI-driven insights forecast maintenance needs, reducing downtime.
Optimized Asset Lifecycle:
- Predictive analytics help determine the optimal time for asset upgrades or replacements, maximizing ROI.
Blockchain for Data Security
Tamper-Proof Records:
- Blockchain integration offers immutable records of asset transactions, bolstering data security and regulatory compliance.
Transparent Audits:
- Enhanced audit transparency reduces the risk of fraud and data manipulation.
Conclusion
Implementing an asset tagging system is a strategic investment that can dramatically enhance asset visibility, operational efficiency, and overall financial performance. By following this comprehensive, step-by-step approach—from defining objectives and performing a detailed audit to integrating with your ERP and planning for continuous improvement—organizations can build a robust, scalable system. As emerging trends like IoT, AI, and blockchain continue to evolve, they promise to further refine asset tracking, ensuring that your organization remains agile and ahead of the curve.
Re-examine your current asset management practices and consider a comprehensive asset tagging system that not only meets today’s needs but is also adaptable for future advancements.
FAQs
Q. What is an asset tagging system?
A. An asset tagging system is a method used to assign unique identification codes to physical assets, typically in the form of barcode, QR code, or RFID tags. These tags are affixed to assets to enable tracking, management, and verification throughout their lifecycle. Asset tagging helps organizations monitor asset movement, perform audits, and reconcile data with their asset registers efficiently.
Q. How do asset tagging systems integrate with ERP or accounting software?
Modern asset tagging systems, like those offered by AssetCues, can seamlessly integrate with ERP to automate asset data updates. Through APIs or data synchronization tools, scanned asset information—such as location, status, and condition—can be linked to the organization’s financial asset register, enabling accurate depreciation calculation and audit compliance in systems like SAP, Oracle, or other ERPs.
Q. What industries benefit the most from asset tagging systems?
Industries with large volumes of physical assets benefit significantly from asset tagging systems. These include: Manufacturing, Healthcare, Education, IT & Technology, Government & Public Sector.
Q. How does AssetCues help with asset tagging and tracking?
AssetCues offers a SaaS-based solution designed specifically for fixed asset tagging and physical verification, using RFID, barcode, or QR technologies to ensure accurate asset tracking and management.




