Introduction
Effective asset management is crucial for organizations to efficiently track, monitor, and maintain their physical assets. Whether it’s equipment, tools, machinery, or IT assets, ensuring each asset is uniquely identifiable improves efficiency. It also reduces losses and meets compliance requirements.
Asset marking plays a pivotal role by providing each asset with a unique identification number. This method connects physical assets to a digital asset register, enabling accurate tracking. Marking assets with identifiable numbers—such as barcodes, RFID tags, or direct engravings—minimizes errors and prevents theft. It ensures assets are consistently accounted for.
What is Asset Marking?
- Asset marking refers to the process of assigning a unique identifier to physical assets, typically through visible markings or asset tags. These identifiers include serial numbers, asset numbers, or equipment numbers. They are affixed to the asset in various forms. These include nameplates, barcode tags, QR code tags, RFID tags, or direct engravings. This system links each physical asset to its digital record in an asset management system. It enables businesses to track, manage, and monitor assets effectively. Businesses can track assets throughout their lifecycle using this system.
- The primary purpose of asset marking is to simplify asset tracking by making it easier to identify and locate assets in real time. Each asset marked with a distinct identifier allows organizations to quickly update asset registers. It also helps conduct regular audits and ensures assets are accurately accounted for
- In addition, asset marking plays a critical role in securing assets. It prevents theft and unauthorized usage. This method offers an efficient and cost-effective solution for organizations. It helps streamline asset management practices and ensure all assets are properly tracked and maintained.
Asset Marking Methods
Various asset marking methods cater to different asset types and tracking requirements. Below are the four most commonly used methods for asset marking:
-
Direct Marking on Asset
Direct marking involves engraving, etching, stamping, or laser marking a unique identifier directly onto the asset. This highly durable method is ideal for permanently identifying high-value or critical assets. These assets endure harsh conditions or require long-term tracking. The identifier is physically marked onto the asset, making it difficult to remove or tamper with. This offers an added layer of security.
-
Name Plate Based Identification
Nameplates are metal or plastic plates attached to assets, displaying essential information like serial numbers. They also include manufacturer details and compliance codes. This method is effective for easily identifying assets. It may not require a permanent or tamper-resistant marking. Nameplates are primarily used for compliance and maintenance purposes. However, they are considered more conventional compared to modern methods like barcodes or QR codes.
-
Barcode/RFID Tagging for Automated Reading of Numbers
Barcode and RFID tagging methods provide automated asset identification by allowing machines to read the asset’s unique identifier. Barcodes are printed on tags that can be scanned through line of sight. RFID tags can be read remotely without direct contact. These technologies enable fast scanning and real-time updates. They are ideal for environments requiring frequent tracking and audits.
-
BLE/GPS Tagging for Active Tracking
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) and GPS tags offer real-time tracking for assets that require continuous monitoring, particularly those that are location-sensitive. BLE tags communicate via short-range Bluetooth signals, while GPS tags use satellite signals to provide geolocation data. These methods are perfect for tracking high-value or mobile assets that need constant monitoring.

Not sure which Asset Marking method is right for you?
Not sure which Asset Marking method is right for you?
Our experts can help choose the best fit for your industry and assets.
Benefits of Asset Marking
Asset marking provides a range of benefits that streamline asset tracking and enhance overall management efficiency. Some of the key advantages include:
-
Improved Accuracy in Asset Tracking
By assigning a unique identifier to each asset, businesses can reduce errors typically associated with manual tracking. Asset marking ensures assets are consistently accounted for, enabling real-time updates to asset registers. This minimizes the risk of misidentification or misplacement.
-
Reduced Asset Loss, Theft, and Mismanagement
Clear and visible asset identification plays a crucial role in preventing theft and unauthorized usage. When each asset is uniquely identifiable, it becomes much harder for assets to be misplaced, lost, or stolen. Their movements can be tracked with ease.
-
Enhanced Compliance and Audit Efficiency
Asset marking simplifies physical asset audits by making it easier to identify, locate, and verify assets. With clearly marked assets, auditors can quickly scan or inspect items to confirm their presence and condition. This results in faster, more efficient audits. This convenience minimizes downtime and reduces the resources required for manual verification.
-
Efficient Asset Management
Asset marking allows businesses to manage their assets more efficiently throughout their lifecycle. By improving tracking accuracy and reducing manual administrative tasks, organizations save time, optimize operations, and focus on strategic activities.
-
Cost-Effective Solution
Compared to traditional manual tracking methods or less efficient asset management systems, asset marking is a cost-effective solution. It reduces the need for manual data entry, prevents asset loss, and lowers costs related to mismanagement and administrative inefficiencies.
Learn more about the 6 Reasons Why Tagging of Assets is Important>>
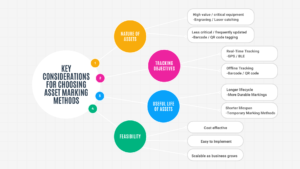
Key Considerations for Choosing an Asset Marking Method
Selecting the right asset marking method depends on several factors that ensure the method aligns with business needs and asset requirements. Some of the key considerations when choosing an asset marking method include:
-
Nature of Assets and Their Usage
The type of asset and its usage play a significant role in determining the best marking method. High-value assets or critical equipment may require durable and permanent markings, such as engraving or laser etching. Less critical or frequently updated assets might benefit from more flexible options like barcode or QR code tagging.
-
Tracking Objectives
Different asset marking methods serve different tracking objectives. For example, if real-time tracking is a priority, technologies such as GPS or BLE tagging would be more suitable. For simpler, offline tracking, methods like barcode or RFID tagging can be more effective. The chosen marking method should match the desired level of tracking automation and frequency of updates.
-
Useful Life of the Asset
The useful life of an asset plays a role in determining the longevity of the asset marking. Assets with a longer lifecycle, such as machinery or vehicles, require more durable markings. Assets with a shorter lifespan, such as office equipment or IT devices, can use temporary marking methods like stickers or labels.
-
Feasibility
Feasibility involves evaluating the practical aspects of implementing an asset marking system. This includes considerations such as cost, ease of implementation, and the complexity of integrating the marking method into existing asset management systems. The method chosen should be cost-effective, easy to apply, and scalable as the business grows.
Implementing Asset Marking
Successfully implementing an asset marking system requires careful planning and execution to ensure a smooth transition and long-term effectiveness. The following steps outline the key components of an effective asset marking implementation:
-
Identify Assets and Select Suitable Marking Techniques
The first step in implementing asset marking is identifying which assets require marking. This involves evaluating the value, usage, and location of each asset to determine the appropriate marking method. Once identified, businesses can select suitable marking techniques based on factors like durability, visibility, and tracking requirements.
-
Integration with Asset Management Systems
After selecting the marking method, it’s essential to integrate the asset marking system with the organization’s asset management software. This integration ensures that each marked asset is linked to a digital record, enabling real-time tracking, updates, and audits. The integration process may involve software customization or the use of specialized tools. This ensures seamless data flow between the marking system and asset management software.
-
Employee Training and Awareness
Proper training is crucial to ensure the successful adoption of asset marking. Employees should be educated on the purpose and benefits of asset marking. They must learn how to correctly apply and scan asset markings. This training should also cover using asset management software to track and update asset information. It ensures consistency and accuracy across the organization.
-
Regular Monitoring and Maintenance
Once businesses implement the asset marking system, they should establish a routine to monitor and maintain the markings. They must regularly check the condition of asset tags or markings to ensure readability and durability. Businesses should also conduct regular audits to verify proper asset accounting and keep asset data updated.
Asset marking is a part of asset tagging. Learn how to implement complete system in our published comprehensive guide – “Implementing Asset Tagging System: A Comprehensive Guide”
Looking to implement this kind of Asset Marking in your organization?
Schedule a Demo today!
Looking to implement this kind of Asset Marking in your organization?
Schedule a Demo today!
History of Asset Marking
The practice of asset marking has evolved over centuries, with early methods focusing on basic identification and ownership marking. As industries grew and technology advanced, so did the techniques used to identify and track assets. Below is an overview of the history of asset marking and how it has developed over time:
-
Early Beginnings: Simple Identification Marks
The earliest forms of asset marking date back to ancient civilizations. Tools and property were marked with symbols, engravings, or stamps to indicate ownership. These markings were rudimentary but effective in distinguishing valuable items and preventing theft, particularly in trade and agricultural societies.
-
Industrial Revolution: Expansion of Marking Methods
During the Industrial Revolution, as manufacturing and production expanded, the need for more sophisticated asset tracking became apparent. Factories began marking their machinery, tools, and equipment with serial numbers and other identifiers. This helped manage inventory and ensure the longevity of their assets. This period saw the rise of metal name plates and hand-stamped identification as methods of marking critical equipment.
-
20th Century: The Advent of Barcode Technology
The 20th century brought about significant advancements in asset marking, particularly with the advent of barcode technology. Introduced in the 1970s, barcodes revolutionized asset tracking by enabling faster and more accurate identification. The ability to scan barcodes quickly and efficiently marked a shift toward automation, reducing the reliance on manual tracking systems.
-
Modern Day: RFID, QR Codes, and Beyond
In recent decades, asset marking has evolved with the introduction of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags and QR (Quick Response) codes. These technologies enable wireless, real-time tracking, allowing businesses to monitor assets remotely and faster. Innovations like GPS tracking and BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) tags have further enhanced asset marking capabilities. They provide real-time geolocation data, enabling businesses to track mobile and high-value assets.
Looking to choose the right technology for your organization, Read our blog on “Asset Tracking Technologies: 5-Step Guide to the Right Choice“
Future Trends in Asset Marking
As technology continues to advance, the field of asset marking is evolving rapidly. Here are some key trends shaping the future of asset marking and asset tracking:
-
Technological Advancements in BLE, GPS, and IoT-Enabled Systems
The future of asset marking is closely tied to the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT-enabled systems will provide greater real-time tracking capabilities by incorporating sensors and advanced communication technologies. These include Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) and GPS. These technologies allow businesses to track assets in real-time, including mobile assets or those located in remote or difficult-to-reach areas. As IoT becomes more integrated into asset management systems, businesses will gain enhanced visibility into their asset’s location and condition.
-
Increased Use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Asset Tracking and Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of asset marking and tracking. AI can automate asset tracking processes, analyze vast amounts of asset data, and provide predictive insights into asset lifecycle management. By leveraging AI, businesses can proactively address issues like asset maintenance and optimize asset utilization. This improves decision-making, leading to better resource management and cost savings.
-
Integration of Augmented Reality (AR) for Asset Identification
Augmented Reality (AR) is emerging as a valuable tool for asset identification and tracking. Through AR devices or mobile apps, users can scan physical assets and access detailed information instantly. This includes asset status, maintenance history, and location. AR enhances the user experience, making asset tracking more intuitive and efficient. It has the potential to revolutionize industries like logistics, manufacturing, and healthcare.
-
Blockchain for Secure Asset Tracking
Blockchain technology, known for its ability to securely record transactions, is gaining attention in the asset management sector. By using blockchain to store asset data, organizations create tamper-proof digital records. This ensures the integrity of their asset tracking systems. This can enhance security, reduce fraud, and improve transparency, particularly for high-value assets or assets that require strict regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
Asset marking plays a crucial role in streamlining asset tracking and management. It enables businesses to track, monitor, and maintain their physical assets more efficiently. By assigning unique identifiers to assets, organizations can reduce errors, enhance security, improve compliance, and optimize asset management practices. Moreover, emerging technologies such as IoT, AI, AR, and blockchain are increasingly shaping the future of asset marking. These technologies promise to revolutionize asset tracking by offering greater automation, improved accuracy, and enhanced security.
As businesses prioritize operational efficiency and risk management, adopting modern asset marking methods becomes crucial. Consequently, these methods will improve asset management practices and help maintain a competitive edge. By investing in the right asset marking system, businesses enhance asset visibility. Furthermore, it provides long-term benefits that drive business growth and sustainability.
Ready to implement a robust Asset Marking and Tracking solution?
Ready to implement a robust Asset Marking and Tracking solution?
FAQs
Q. What is asset marking?
A. Asset marking assigns a unique identifier to each physical asset using visible markings or asset tags. This process links every asset to its digital record in the asset management system. As a result, you can track, manage, and monitor assets efficiently throughout their lifecycle. Asset marking improves tracking accuracy, reduces losses, and simplifies audits for organization.
Q. What is an asset marker?
A. Asset markers are small, adhesive-backed labels and markers that typically display a company name and logo, serial numbers and barcodes.
Q. What information is typically included on an asset tag or marking?
A. Asset tags usually display a unique asset ID, serial number, or equipment number. You may also include asset description, manufacturer details, and acquisition date. This information ensures each asset is easily identified and tracked in the asset management system.
Q. Can asset marking be integrated with software systems?
A. Yes. Modern asset marking methods like RFID and barcodes are designed to integrate seamlessly with asset management software, enabling automated tracking, real-time updates, and reporting.




