RFID costs more upfront due to expensive tags and readers. However, it reduces labor and saves time. In contrast, barcodes are cheaper but require more manual effort.In the world of asset tracking, barcodes and RFID tags are the most widely used automation technologies. They’re both respected and adopted across multiple industries and various asset management use cases.
However, a million dollar question that organizations always face is → which is a better technology out of the two for their asset management transformation?
While we cannot answer the question with a this or that, we can explain these two technologies for what they are, explain their differences and put out the applications where they work best.
In this article, we’ll dive into the nuts and bolts of RFID and barcode technologies, exploring how they work, their advantages and drawbacks, and how to decide which is right for your Asset tracking objective.
Let’s get started!
What is RFID?
In the simplest of terms, RFID (Radio Frequency Edentification) technology uses radio waves and RFID tags to track assets. After RFID tags are affixed to your assets, they can be tracked using RFID readers without requiring a line of sight, even if they’re at a farther distance.
Check out this extensive article we’ve written on “RFID Asset Tracking – Transforming Asset Management”
How RFID Technology Works
When an RFID tag gets close to an RFID reader, the reader sends out a signal. The tag picks up this signal and responds with its unique information. This process happens in a fraction of a second — making it incredibly efficient.
Components of an RFID System
- Tags: These come in two flavors—passive (no battery, powered by the reader’s signal) and active (with a battery for longer range and more data).
- Readers: Devices that scan the tags and gather information.
- Antennas: Help in broadcasting and receiving signals from the tags.
- ERP or Asset Tracking Software: Data collected from RFID tags is processed and stored in an ERP or tracking software.
Types of RFID
- Passive RFID: Perfect for when you need something simple and cost-effective. These tags are great for tracking items that don’t move too far from the reader.
- Active RFID: These are your go-to for high-value assets or when you need a longer read range. They’re equipped with batteries, allowing them to transmit signals over greater distances.
Learn more about Active & Passive Tracking in our blog – “Active vs. Passive Tracking: Which Asset Tracking Technology is right for you?”
Primary Solutions of RFID
- Automation of Asset Inventory: A common use case of passive RFID, enterprises can easily automate their asset inventory by affixing passive RFID tags and scanning them using mobile readers.
- Monitoring Asset Movement: Widely used in IT asset management, assets that frequently move in and out of premises can be tracked using a check-in and check-out system.
- Real-time Location Tracking (RTLS): In industries where live location of assets is critical for operations, active RFID tracking systems can be used to establish real-time location tracking.
Contact our team for a customized quote on implementing RFID asset tracking in your organization
Talk to our team for a quote for implementing RFID Asset tracking in your organization
Contact our team for a customized quote on implementing RFID asset tracking in your organization
Talk to our team for a quote for implementing RFID Asset tracking in your organization
What is Barcode?
Barcodes might seem old-school compared to RFID, but they’re still a powerhouse in the asset tracking world. A barcode is a series of lines and spaces that represent data, which a scanner reads.
Read more about Barcode/QR code Asset Tracking in our blog post – “Barcode & QR Code Asset Tracking Made Easy: Scalable Solutions for Finance, IT & Operations”.
How Barcode Technology Works
A barcode scanner shines a light on the barcode, which reflects back into the scanner. The scanner interprets the reflected light into data. It’s a bit like translating a visual language into useful information. Today, most barcode scanning is done via mobile phones as they have the capability to scan and read the data.
Components of a Barcode System
- Labels: These are the printed codes that go on assets.
- Scanners or Mobile phones: Devices that read the barcodes and input the data into your system.
- Software: Manages and processes the data collected from barcodes.
Types of Barcodes
- 1D Barcodes: The classic lines-and-spaces format, useful for straightforward applications.
- 2D Barcodes (QR Codes): These can store more information and are often used for more complex needs.
- The difference: The biggest difference between both the barcodes is the angle of reading. If it’s 1d then you need to have the reader straightly pointed to the barcode. If it’s 2d, then the barcode can be read at a tilted angle.
RFID Vs Barcode Asset Tracking: Key Differences
| Feature | RFID | Barcode |
| Data Storage Capacity | High (up to 64 kilobits) | Low (limited to a few characters) |
| Scanning Range | Up to 20 meters | 1-2 meters |
| Scanning Speed | Multiple tags simultaneously | One tag at a time |
| Line of Sight Required | No | Yes |
| Durability | High; withstands harsh environments | Low; susceptible to damage |
| Cost | Higher initial and ongoing costs | Lower initial costs |
| Implementation Complexity | Higher for large systems | Simpler and quicker |
| Data Security | Can be encrypted | Less secure; easier to duplicate |
Technology and Functionality
- Data Storage Capacity: Active RFID tags can hold more data whereas passive RFID tags hold very limited data. Barcodes, on the other hand, have much more limited data when compared to RFID tags. Think of RFID as a mini hard drive compared to a barcode’s sticky note.
- Scanning Range and Speed: RFID can scan hundreds of tags in seconds, while barcodes are more of a one-at-a-time process. RFID can even read through boxes and containers, while barcodes need a direct line of sight.
- Line of Sight Requirements: RFID doesn’t need to see the tag directly, making it more flexible in various scenarios.
Cost Comparison
- Initial Setup Costs: Barcodes are budget-friendly, but RFID can be a bit more expensive upfront. The major difference comes in the reader costs. For barcodes, you can leverage mobile phones to scan and read. However, think of RFID as an investment in efficiency and speed.
- Long-Term Operational Costs: While RFID has higher initial costs, it often leads to significant savings over time due to reduced labor and error rates.
- Maintenance and Scalability: Barcodes are simple and cheap to maintain. RFID requires a bit more upkeep but offers greater scalability and flexibility.
Durability and Reliability
- Environmental Tolerance: RFID tags are built to endure harsh conditions, while barcodes can be affected by dirt and damage. RFID tags can even have sensors for additional data like temperature.
- Error Rates and Accuracy: RFID systems are less prone to errors compared to barcodes, which can get damaged or smudged.
Data Security
- Vulnerabilities and Protection Mechanisms: RFID tags can be encrypted and are harder to duplicate, offering better security compared to barcodes which can be easily copied.
Pros and Cons of RFID
Advantages of RFID
- Faster Data Capture and Real-Time Updates: RFID can handle asset inventory quickly, keeping your data current and accurate.
- Enhanced Data Storage and Retrieval: More information can be stored on RFID tags, allowing for detailed asset tracking.
- Capabilities in Harsh Environments: RFID tags are durable and can withstand tough conditions, making them ideal for challenging environments.
Disadvantages of RFID
- Higher Initial Costs: The upfront investment can be higher compared to barcodes but yet the ROI is better.
- Complexity of Implementation: Depending on the type of RFID tracking you choose, setting up RFID usually takes a little longer than barcode tracking. Many-a-time passive RFID setup takes as long as a barcode setup.
- Gaining Auditor Confidence: While line of sight is not required in RFID tracking, it can be challenging when your auditor needs physical verification of your assets. It’s quite important to gain your auditing team’s approval before implementing an RFID asset tracking system.
Pros and Cons of Barcode
Advantages of Barcode
- Low Cost and Ease of Implementation: Cost of Barcodes is low compared to RFID and easy to set up.
- Compatibility and Standardization: Though RFID systems have gained quite a popularity in recent years, barcodes are still universally recognized and widely used across multiple industries.
- Wide Adoption and Familiarity: Most people are familiar with barcode technology, making it a comfortable choice for many businesses.
Disadvantages of Barcode
- Limited Data Storage: Barcodes can only hold a small amount of data.
- Need for Line-of-Sight Scanning: Scanning barcodes requires a direct view, which can be a limitation in some settings.
- Susceptibility to Damage and Wear: Barcodes can get damaged or dirty, leading to read errors.
RFID vs Barcode: Which is Right for Your Asset Tracking?
Factors to Consider
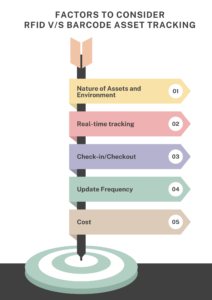
- Nature of Assets and Environment: Assess the types of assets you’re tracking and the environment they’re in. For example, if assets are highly mobile, you may want to consider RFID whereas if they have little movement then barcodes would be a better option.
- Real-time tracking: If your objective is to track your assets in realtime and find their location, then RFID technology would be the ideal choice.
- Check-in/Checkout: If your assets move outdoors quite frequently, you need to track the check in and checkouts, then RFID technology would be the ideal solution. If it’s a static asset then you can opt for barcode technology.
- Update Frequency: How frequently do you need the status of your asset’s location or availability? How often do you need to verify your asset? – If the answer is frequent then RFID is the way to go.
- Cost: Last but not the least, you should factor in the costs for the infrastructure. Active RFID, passive RFID and barcode come in different price points. Depending on your needs and budget, choose the one that aligns with your asset management goals.
There may be more factors to consider which are unique to your company’s needs. You may also want to consider a combination of technologies depending on your objectives.
Remember to always align the technology with your business objectives and operational needs. Think about how your needs might grow and which technology will scale with you.
Not sure which asset tracking solution fits your scenario?
Compare solutions with our experts to get a personalized recommendation.
We can help evaluate your specific needs and suggest the best mix of technologies for your situation.
Not sure which asset tracking solution fits your scenario?
Compare solutions with our experts to get a personalized recommendation.
We can help evaluate your specific needs and suggest the best mix of technologies for your situation.
Future Trends in RFID and Barcode Technologies
Advancements in RFID
- Integration with IoT and AI: RFID is becoming smarter with integrations that enhance data analytics and automation.
- Innovations in Tag Technology and Applications: Expect to see more advanced tags with additional functionalities.
- Better Costs: With the evolution of RFID ecosystem, the cost is expected to go down, covering up the difference with Barcode technology
Advancements in Barcode
- Digital Transformation and Mobile Scanning: Barcodes are evolving with mobile technology, making them even more versatile.
- Advances in 2D Barcodes and QR Codes: New barcode types are emerging with enhanced data capabilities and applications.
Conclusion
Choosing between RFID and barcode technology depends on your specific business needs and operational goals. RFID offers superior data storage, faster processing, and better durability, making it ideal for complex and high-volume operations. Barcodes are cost-effective and straightforward, suitable for simpler tracking needs. Evaluate your requirements carefully to determine the best fit for your business and consider reaching out to experts for tailored advice.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. What are the main differences between RFID and Barcode?
A. RFID can read multiple tags simultaneously without line of sight, while barcodes require direct visibility and read one at a time. RFID tags have higher data storage and can function in harsh environments, whereas barcodes are simpler and less expensive.
Q. Is it better to use RFID than bar code?
A. Yes, RFID is better for fast, automated, and large-scale asset tracking. However, barcodes work well for simple, low-cost needs. So, choose based on your organization and tracking complexity.
Q. Can RFID and Barcode be used together?
A. Yes, RFID and barcode technologies can be used together to leverage the benefits of both systems. For instance, RFID can automate data capture, while barcodes can provide human-readable information.
Q. How much does RFID cost compared to barcode?
A. RFID costs more upfront due to expensive tags and readers. However, it reduces labor and saves time. In contrast, barcodes are cheaper but require more manual effort.
Q. What are the security concerns with RFID?
A. RFID tags can be vulnerable to unauthorized reading and tampering. Security measures such as encryption and access controls can help mitigate these risks.
Q. Which technology is better for tracking assets?
A. The choice between RFID and barcode depends on your specific needs, including the complexity of assets, budget, and environmental factors. RFID offers advantages in speed and automation, while barcodes are cost-effective and straightforward.




