Asset verification is essential for reliable financial reporting. Auditors must confirm that fixed assets (machinery, buildings, vehicles, etc.) exist, are properly valued, and comply with accounting standards. By verifying assets, organizations prevent ghost assets and misreporting, thereby supporting strong compliance with IFRS/GAAP and regulatory rules. In practice, verification of fixed assets in auditing ensures compliance with IAS 16 and ASC 360 to make sure all assets are correctly valued and documented.
For a deeper understanding of the end-to-end process, explore our Fixed Asset Verification: A Complete Guide to Physical Asset Audits
Why Asset Verification Matters in Auditing
Accurate Financial Reporting:
Verification confirms that all assets on the balance sheet truly exist and are correctly valued. This prevents overstatement or understatement of asset balances. Auditors check depreciation methods per accounting standards (e.g. IAS 16) to ensure values reflect usageifrs.org.
Regulatory Compliance:
International standards (IAS 16, 36; ASC 360, etc.) require regular asset reviews. For instance, IFRS allows a revaluation model (fair value basis) when a reliable market price exists ifrs.org, while US GAAP mandates historical cost. Auditing asset verification enforces these rules, ensuring firms comply with IFRS/GAAP and tax laws.
Fraud Prevention:
Systematic checks, such as physical counts and documentation reviews, reveal theft or misclassification. As a result, fixed asset audits help identify ghost or obsolete assets inflating records. Moreover, strong internal controls and audit procedures enhance the reliability of financial statements. Together, these practices improve transparency and support accurate reporting.
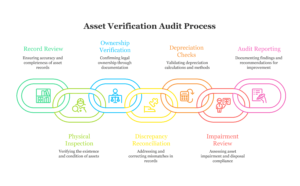
Key Steps in an Asset Verification Audit
Review Asset Records:
Obtain the fixed asset register and reconcile it with the general ledger. Ensure each acquisition and disposal is recorded. Confirm assets are categorized correctly and complete.
Physical Inspection:
Select assets (often by risk or materiality) and physically inspect them. Verify the existence and condition of each asset listed in the records. This step catches missing or impaired items.
Ownership and Documentation:
For a sample of assets, first review legal documents like titles, invoices, and contracts. Then, confirm the company’s valid ownership and match costs to recorded values. Additionally, check for third-party liens or encumbrances and ensure they are properly disclosed. This process strengthens audit accuracy and legal compliance.
Reconcile Discrepancies:
Compare the results of physical counts with the asset register and ledger. Any mismatch (e.g. unrecorded disposals or unexpected items) should be investigated and corrected. Update records to reflect actual assets on hand.
Depreciation and Valuation Checks:
Recalculate depreciation for sample assets to ensure accuracy and policy alignment. Then, review useful lives and salvage values based on internal guidelines. Also, verify that depreciation methods follow IFRS or GAAP and match asset usage. If needed, justify and document any changes or estimates clearly
Read more about – How Physical Asset Verification can Ensure Accurate Depreciation?
Impairment and Disposal Review:
Assess any indications of impairment (poor condition, obsolescence) and verify compliance with standards (IAS 36/ASC 360). Ensure disposals are authorized, recorded in the correct period, and any gains or losses are properly calculated. For example, IFRS 5 requires proper accounting when assets are held for sale.
Audit Reporting:
Document all findings and discrepancies in a clear report. Include recommendations to strengthen controls (e.g. fixing misclassified items, updating policies) and ensure transparency to management and regulators. This report serves as proof that the fixed assets were audited thoroughly.

Best Practices and Controls for Asset Verification
Strong Internal Controls:
Require authorization for all asset purchases and disposals. Maintain segregation of duties between those who record assets and those who handle them.
Maintain a Robust Asset Register:
Keep an up-to-date, detailed register (or general ledger) that includes each asset’s location, cost, acquisition date, depreciation, and owner. This register is the primary source for audits.
Regular Physical Counts:
Conduct wall-to-wall inventories or cycle counts (periodic spot-checks) to reconcile physical assets with records. Frequent counts quickly surface missing or misplaced assets.
Advanced Tracking Technology:
Use barcodes, RFID tags or IoT sensors to track assets in real time. Modern tools “make tracking easier and keep records accurate”. For example, fixed assets scanned via RFID can be instantly logged into the system during the audit.
Ongoing Staff Training:
Ensure asset managers and auditors are trained on current accounting policies and technology. Well-trained teams avoid errors in tagging, counting, and recording assets.
Utilize Audit Software:
Automated asset audit tools (such as AssetCues’ Asset Verification app) digitize the process. They can scan barcodes/RFID to update the register, generate exception reports, and speed reconciliation, reducing manual work and errors.
Technology and Tools for Asset Verification
Modern technology greatly enhances audit efficiency:
According to a PwC study, 90% of companies see major efficiency gains in audit and control functions via tech adoption—highlighting the growing role of automated tools in financial verification.
RFID & Barcode Scanners:
Devices automate data capture. Auditors can scan barcoded assets instead of manual counts. This speeds up physical inspection and reduces errors. (For example, RFID tags broadcast asset IDs for instant logging.)
Mobile Audit Apps:
Dedicated apps (like those from AssetCues) let auditors perform real-time verification on tablets/smartphones. They can scan assets, record photos, and sync instantly with the asset register, accelerating the audit cycle.
IoT Sensors and Drones:
For hard-to-reach assets (remote sites, warehouses), drones or sensors can collect location and condition data, feeding it into the audit system.
Analytics Software:
Data analytics can flag anomalies (e.g. assets with no depreciation charged) or identify outliers. Automated reconciliation tools compare records and highlight mismatches, so auditors focus on exceptions.
By integrating these tools, finance teams can conduct faster, more accurate asset audits. AssetCues’ platform, for example, ties directly to your general ledger and asset register, automating reconciliation and even generating report summaries – saving hundreds of hours during audit season.
Try Assetcues for Audit
Schedule a demo to see how our asset verification software automates your next audit.
Book a Free Consultation with Our Asset Audit Experts
Talk to AssetCues professionals to identify the best verification method for your organization
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Ghost and Missing Assets:
Without verification, non-existent (“ghost”) assets may remain on the books. Prevent this by rigorous physical checks and cross-verifying with purchase logs.
Incomplete Records:
Outdated or inaccurate registers lead to discrepancies. Maintain documentation (invoices, titles) and promptly update disposals. Reconcile records as soon as changes occur.
Multiple Systems:
If asset data is siloed (e.g., separate IT and Facilities databases), inconsistencies arise. Integrate or standardize systems so all asset types feed into one register.
Asset Accessibility:
Some assets (off-site or leased equipment) are hard to verify. Plan audits when assets are on-site or use remote technologies (drones, cameras) to inspect them.
Complex Assets:
Machinery with many parts or long-lived projects can be tricky. Break complex assets into components in the register and audit each part’s status and valuation.
Careful planning and use of technology (see above) help overcome these hurdles. Training audit teams on best practices also ensures fewer errors.
Conclusion: The Imperative of Regular Asset Verification
Verification of assets in auditing is a multifaceted process that safeguards financial integrity. By following structured procedures – from physical counts to depreciation testing – organizations make sure their financial statements truly reflect reality. Aligning verification practices with accounting standards (IAS 16, 36, IFRS 5, ASC 360, etc.) and adopting new audit technologies closes gaps that outdated methods might miss.
A culture of continuous improvement and automation boosts compliance and operational efficiency. Regular use of tools like AssetCues’ audit software ensures consistent, accurate asset tracking. As a result, thorough fixed asset audits build stakeholder confidence and trust. They also support transparent and accurate financial reporting across the organization.
Download Our Fixed Asset Audit Checklist
Ensure you haven’t missed any critical steps in your asset verification process.
Download Our Fixed Asset Audit Checklist
Ensure you haven’t missed any critical steps in your asset verification process.
FAQs
Q: What are the main steps in verifying fixed assets during an audit?
A: Key steps include reviewing the asset register and ledger, then conducting a physical asset count. Next, verify ownership documents like titles and invoices for selected assets. After that, reconcile any differences and test depreciation for accuracy. Together, these steps provide assurance that fixed assets are properly reported.
Q: How does asset verification impact financial audits and compliance?
A: Asset verification directly affects the audit opinion. It ensures that fixed assets on the balance sheet are real, properly valued, and compliant with accounting standards. By verifying assets, auditors reduce risk of material misstatements (e.g. from ghost assets or incorrect depreciation). This makes financial statements more reliable.
Q: What technologies assist with asset verification in auditing?
A: Modern tools significantly speed up and simplify asset audits for organizations. RFID tags and barcode scanners help auditors quickly scan and record assets. Mobile audit apps like AssetCues automate data capture and real-time reconciliation. Technologies like IoT sensors and drones improve reach, accuracy, and overall audit efficiency.
Q: Can you give an example of an asset verification audit procedure?
A: Sure. For example, auditors may select 10% of assets like computers for review. They physically verify each item, check asset tags, and match register details. Then, they confirm correct depreciation and investigate any missing or incorrect data. This sampling approach, along with reconciliations, ensures accurate financial reporting of fixed assets
About Author